wordpress进阶教程(三十九):wordpress输出bootstrap的菜单结构
现在自适应网页(即常说的响应式设计,一个网页在PC平板手机上显示不同的布局)用的越来越多,然而,对于大多数人来说,写一个自适应的网页并非易事,于是有了bootstrap。
Bootstrap是twitter的工程师利用业余时间制作推出的一个开源的用于前端开发的工具包,即里面已经写好了css js,你只需要引入它的js和css,然后根据要求,给网页的div添加相应的class属性,即可制作一个响应式网页。
说实话,bootstrap很方便,作者使用过一次,但是有一个缺点,那就是你需要引入bootstrap的框架的css和js,然而这个css里面,有很多代码都是你用不到的,这样就会产生很多冗余代码,而去除css的冗余代码绝对是个体力活,所以作者用过一次就不用了。
将bootstrap应用到wordpress上也很简单,唯一可能有困难的就是菜单,因为bootstrap的菜单有他自己的结构和属性,最新的菜单演示页面如下:http://v3.bootcss.com/examples/navbar/
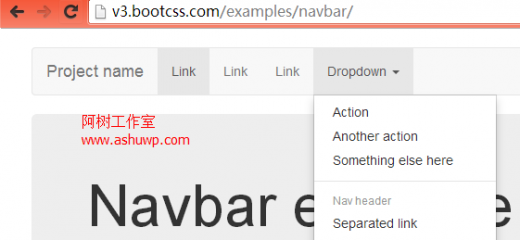
查看网页源文件,可以看到菜单的结构大概是这样
- <ul =“nav navbar-nav”>
- <li =“active”><a href=“#”>Link</a></li>
- <li =“dropdown”>
- <a href=“#” =“dropdown-toggle” data-toggle=“dropdown”>Dropdown <b =“caret”></b></a>
- <ul =“dropdown-menu”>
- <li><a href=“#”>Action</a></li>
- <li><a href=“#”>Another action</a></li>
- </ul>
- </li>
- </ul>
要在wordpress上实现这个菜单结构看似不难,其实,里面Dropdown后面的<b class=”caret”></b>对应网页中下拉菜单的那个到三角形,以及二级菜单的ul标签的class属性。除非你把菜单写死,否则使用wp_nav_menu函数是无法输出这两个内容的。
那要怎么办呢?
wordpress的wp_nav_menu函数参数如下:
- <?php
- $defaults = (
- ‘theme_location’ => ”,
- ‘menu’ => ”,
- ‘container’ => ‘div’,
- ‘container_class’ => ”,
- ‘container_id’ => ”,
- ‘menu_class’ => ‘menu’,
- ‘menu_id’ => ”,
- ‘echo‘ => true,
- ‘fallback_cb’ => ‘wp_page_menu’,
- ‘before’ => ”,
- ‘after’ => ”,
- ‘link_before’ => ”,
- ‘link_after’ => ”,
- ‘items_wrap’ => ‘<ul id=“%1$s” =“%2$s”>%3$s</ul>’,
- ‘depth’ => 0,
- ‘walker’ => ”
- );
- wp_nav_menu( $defaults );
- ?>
其中的walker参数是关键。
更改你的主题菜单输出函数wp_nav_menu的walker参数:
- <?php
- wp_nav_menu( (
- ‘theme_location’ => ‘ashu_menu’,
- ‘depth’ => 2,
- ‘container’ => false,
- ‘menu_class’ => ‘nav navbar-nav’,
- ‘fallback_cb’ => ‘wp_page_menu’,
- //添加或更改walker参数
- ‘walker’ => wp_bootstrap_navwalker())
- );
- ?>
上面代码中walker参数的值是一个类,所以接下来你需要添加这个类,在你的主题functions.php文件中添加下面代码:
或者https://github.com/twittem/wp-bootstrap-navwalker/blob/master/wp_bootstrap_navwalker.php
- <?php
- /**
- * Class Name: wp_bootstrap_navwalker
- * GitHub URI: https://github.com/twittem/wp-bootstrap-navwalker
- * Description: A custom WordPress nav walker class to implement the Bootstrap 3 navigation style in a custom theme using the WordPress built in menu manager.
- * Version: 2.0.4
- * Author: Edward McIntyre – @twittem
- * License: GPL-2.0+
- * License URI: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.txt
- */
- wp_bootstrap_navwalker Walker_Nav_Menu {
- /**
- * @see Walker::start_lvl()
- * @since 3.0.0
- *
- * @param string $output Passed by reference. Used to append additional content.
- * @param int $depth Depth of page. Used for padding.
- */
- start_lvl( &$output, $depth = 0, $args = () ) {
- $indent = str_repeat( “t”, $depth );
- $output .= “n$indent<ul role=”menu” class=” dropdown-menu”>n”;
- }
- /**
- * @see Walker::start_el()
- * @since 3.0.0
- *
- * @param string $output Passed by reference. Used to append additional content.
- * @param object $item Menu item data object.
- * @param int $depth Depth of menu item. Used for padding.
- * @param int $current_page Menu item ID.
- * @param object $args
- */
- start_el( &$output, $item, $depth = 0, $args = (), $id = 0 ) {
- $indent = ( $depth ) ? str_repeat( “t”, $depth ) : ”;
- /**
- * Dividers, Headers or Disabled
- * =============================
- * Determine whether the item is a Divider, Header, Disabled or regular
- * menu item. To prevent errors we use the strcasecmp() function to so a
- * comparison that is not case sensitive. The strcasecmp() function returns
- * a 0 if the strings are equal.
- */
- ( strcasecmp( $item->attr_title, ‘divider’ ) == 0 && $depth === 1 ) {
- $output .= $indent . ‘<li role=“presentation” =“divider”>’;
- } ( strcasecmp( $item->title, ‘divider’) == 0 && $depth === 1 ) {
- $output .= $indent . ‘<li role=“presentation” =“divider”>’;
- } ( strcasecmp( $item->attr_title, ‘dropdown-header’) == 0 && $depth === 1 ) {
- $output .= $indent . ‘<li role=“presentation” =“dropdown-header”>’ . esc_attr( $item->title );
- } ( strcasecmp($item->attr_title, ‘disabled’ ) == 0 ) {
- $output .= $indent . ‘<li role=“presentation” =“disabled”><a href=“#”>’ . esc_attr( $item->title ) . ‘</a>’;
- } {
- $class_names = $value = ”;
- $classes = ( $item->classes ) ? () : () $item->classes;
- $classes[] = ‘menu-item-‘ . $item->ID;
- $class_names = join( ‘ ‘, apply_filters( ‘nav_menu_css_class’, array_filter( $classes ), $item, $args ) );
- ( $args->has_children )
- $class_names .= ‘ dropdown’;
- ( in_array( ‘current-menu-item’, $classes ) )
- $class_names .= ‘ active’;
- $class_names = $class_names ? ‘ =“‘ . esc_attr( $class_names ) . ‘”‘ : ”;
- $id = apply_filters( ‘nav_menu_item_id’, ‘menu-item-‘. $item->ID, $item, $args );
- $id = $id ? ‘ id=“‘ . esc_attr( $id ) . ‘”‘ : ”;
- $output .= $indent . ‘<li’ . $id . $value . $class_names .’>’;
- $atts = ();
- $atts[‘title’] = ! ( $item->title ) ? $item->title : ”;
- $atts[‘target’] = ! ( $item->target ) ? $item->target : ”;
- $atts[‘rel’] = ! ( $item->xfn ) ? $item->xfn : ”;
- // If item has_children add atts to a.
- ( $args->has_children && $depth === 0 ) {
- $atts[‘href’] = ‘#’;
- $atts[‘data-toggle’] = ‘dropdown’;
- $atts[‘‘] = ‘dropdown-toggle’;
- $atts[‘aria-haspopup’] = ‘true’;
- } {
- $atts[‘href’] = ! ( $item->url ) ? $item->url : ”;
- }
- $atts = apply_filters( ‘nav_menu_link_attributes’, $atts, $item, $args );
- $attributes = ”;
- ( $atts $attr => $value ) {
- ( ! ( $value ) ) {
- $value = ( ‘href’ === $attr ) ? esc_url( $value ) : esc_attr( $value );
- $attributes .= ‘ ‘ . $attr . ‘=“‘ . $value . ‘”‘;
- }
- }
- $item_output = $args->before;
- /*
- * Glyphicons
- * ===========
- * Since the the menu item is NOT a Divider or Header we check the see
- * if there is a value in the attr_title property. If the attr_title
- * property is NOT null we apply it as the class name for the glyphicon.
- */
- ( ! ( $item->attr_title ) )
- $item_output .= ‘<a’. $attributes .’><span =“glyphicon ‘ . esc_attr( $item->attr_title ) . ‘”></span> ‘;
- $item_output .= ‘<a’. $attributes .’>’;
- $item_output .= $args->link_before . apply_filters( ‘the_title’, $item->title, $item->ID ) . $args->link_after;
- $item_output .= ( $args->has_children && 0 === $depth ) ? ‘ <span =“caret”></span></a>’ : ‘</a>’;
- $item_output .= $args->after;
- $output .= apply_filters( ‘walker_nav_menu_start_el’, $item_output, $item, $depth, $args );
- }
- }
- /**
- * Traverse elements to create list from elements.
- *
- * Display one element if the element doesn’t have any children otherwise,
- * display the element and its children. Will only traverse up to the max
- * depth and no ignore elements under that depth.
- *
- * This method shouldn’t be called directly, use the walk() method instead.
- *
- * @see Walker::start_el()
- * @since 2.5.0
- *
- * @param object $element Data object
- * @param array $children_elements List of elements to continue traversing.
- * @param int $max_depth Max depth to traverse.
- * @param int $depth Depth of current element.
- * @param array $args
- * @param string $output Passed by reference. Used to append additional content.
- * @return null Null on failure with no changes to parameters.
- */
- display_element( $element, &$children_elements, $max_depth, $depth, $args, &$output ) {
- ( ! $element )
- ;
- $id_field = $this->db_fields[‘id’];
- // Display this element.
- ( is_object( $args[0] ) )
- $args[0]->has_children = ! ( $children_elements[ $element->$id_field ] );
- parent::display_element( $element, $children_elements, $max_depth, $depth, $args, $output );
- }
- /**
- * Menu Fallback
- * =============
- * If this function is assigned to the wp_nav_menu’s fallback_cb variable
- * and a manu has not been assigned to the theme location in the WordPress
- * menu manager the function with display nothing to a non-logged in user,
- * and will add a link to the WordPress menu manager if logged in as an admin.
- *
- * @param array $args passed from the wp_nav_menu function.
- *
- */
- fallback( $args ) {
- ( current_user_can( ‘manage_options’ ) ) {
- extract( $args );
- $fb_output = null;
- ( $container ) {
- $fb_output = ‘<‘ . $container;
- ( $container_id )
- $fb_output .= ‘ id=“‘ . $container_id . ‘”‘;
- ( $container_class )
- $fb_output .= ‘ =“‘ . $container_class . ‘”‘;
- $fb_output .= ‘>’;
- }
- $fb_output .= ‘<ul’;
- ( $menu_id )
- $fb_output .= ‘ id=“‘ . $menu_id . ‘”‘;
- ( $menu_class )
- $fb_output .= ‘ =“‘ . $menu_class . ‘”‘;
- $fb_output .= ‘>’;
- $fb_output .= ‘<li><a href=“‘ . admin_url( ‘nav-menus.php’ ) . ‘”>Add a menu</a></li>’;
- $fb_output .= ‘</ul>’;
- ( $container )
- $fb_output .= ‘</’ . $container . ‘>’;
- echo $fb_output;
- }
- }
- }